확률론3-2 : 나이브 베이즈(Naive Bayes)분류기 [in r]
베이즈정리를 모르신다면 아래의 글을 보시길 권장합니다.https://pastryofjsmath.tistory.com/11
확률론3 - 베이즈정리(Bayes Theorem)
나이브 베이즈 분류기법을 설명하기전에 베이즈 정리를 설명하려고 합니다.앞서 베이즈정리를 알기위해 사전지식으로 전확률(Total Prob.)과 분할(Partition)을 알아야합니다. 어려워 보여도 문제를
pastryofjsmath.tistory.com
나이브 베이즈 분류기는 입력변수 간 서로 독림임을 가정으로 시작합니다
조건부 확률의 조건부 독립이 성립해야 합니다.
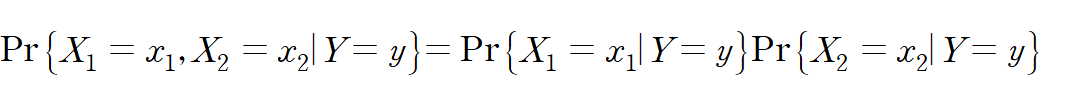
분류모델 성능 측정으로 매우 유명한 타이타닉 데이터 셋으로 해보겠습니다.
제일 먼저, 나이브 베이즈 사용을 위한 패키지를 라이브러리를 해주어야합니다.
install.packages("e1071")
library("e1071")
#titanic<-read.csv()
> titanic %>% summary()
pclass survived sex age
Upper :282 No :618 Length:1043 Min. : 0.1667
Middle:261 Yes:425 Class :character 1st Qu.:21.0000
Lower :500 Mode :character Median :28.0000
Mean :29.8132
3rd Qu.:39.0000
Max. :80.0000
sibsp parch fare embarked
Min. :0.0000 Min. :0.0000 Min. : 0.00 ?: 0
1st Qu.:0.0000 1st Qu.:0.0000 1st Qu.: 8.05 C:212
Median :0.0000 Median :0.0000 Median : 15.75 Q: 50
Mean :0.5043 Mean :0.4219 Mean : 36.60 S:781
3rd Qu.:1.0000 3rd Qu.:1.0000 3rd Qu.: 35.08
Max. :8.0000 Max. :6.0000 Max. :512.33
> titanic %>% str()
'data.frame': 1043 obs. of 8 variables:
$ pclass : Factor w/ 3 levels "Upper","Middle",..: 3 3 2 3 3 2 3 2 1 3 ...
$ survived: Factor w/ 2 levels "No","Yes": 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 2 2 1 ...
$ sex : chr "male" "male" "male" "female" ...
$ age : num 17 30 23 30 29 29 16 36 30 19 ...
$ sibsp : int 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 1 0 0 ...
$ parch : int 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 ...
$ fare : num 7.9 7.22 15.05 8.66 7.92 ...
$ embarked: Factor w/ 4 levels "?","C","Q","S": 4 2 2 4 4 2 4 4 2 4 ...우선 pclass='Lower', sex='female', age=28, sibsp=1, parch=0, fare= 8.88, embarked='Q'인 사람 한명이 탔다고 합니다.
그리고 이 사람의 생존유무를 체크한다고 합시다.
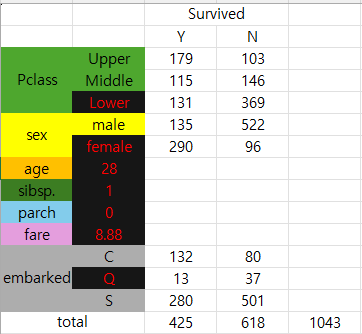
그렇다면 아래와 같이 쓸 수 있습니다.

위의 굵은 글씨는 어떠한 사람이라는 가정하에 생존할 확률을 뜻합니다.
다음줄은 등식을 알고 있어야합니다.
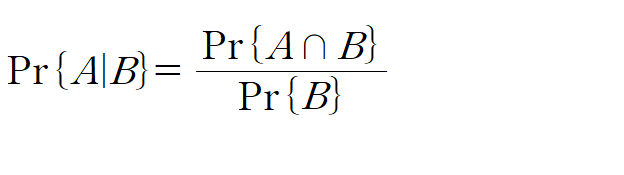
하나씩 보자면 생존여부:Yes 라는 첫줄에서는 위의 등식을 만족합니다 (콤마(,):and,교집합이란 뜻입니다.)
그리고 다음줄은 분자를 생존여부에 따른 조건부 확률을 생존을 가정하에 어떤 사람일 확률로 변형한 모습입니다.
마지막 줄은 조건부 독립이란 성질에 의해 각각의 조건부확률로 바뀐 모습입니다. 이를 생존여부:No인 경우에도 해주어서 각 확률을 비교하여 큰 쪽으로 분류하는 것이 나이브 베이즈 분류기입니다.
nb2 <- naiveBayes(survived ~. , data=titanic_train)
> titanic_test2 <- data.frame(pclass='Lower',sex='female',
+ age=28,sibsp=1,parch=0,
+ fare= 8.88,embarked='Q')
> predict(nb2,titanic_test2)
[1] No
Levels: No Yes
#얼만큼의 확률이 나왔길래 No가 나왔는가?
> predict(nb2,titanic_test2,type='raw')
No Yes
[1,] 0.7049402 0.2950598
#전체 데이터프레임에서의 샘플링을 통한 train/test
sam<-sample(x = 1:1043,size = 800,replace = F)
sam %>% head()
titanic_train <- titanic[sam,]
titanic_test <- titanic[-sam,]
nb2 <- naiveBayes(survived ~. , data=titanic_train)
titanic_test$pred <-predict(nb2,titanic_test[,-2])
#정확도
(titanic_test$survived == titanic_test$pred) %>% mean()
[1] 0.8024691
아래는 다른 예제를 준비해봤습니다.
https://www.kaggle.com/datasets/uciml/mushroom-classification/data
Mushroom Classification
Safe to eat or deadly poison?
www.kaggle.com
cap-shape(갓 모양)
bell:b.종모양, conical:c.원뿔,convex:x.볼록,flat:f.평평,knobbed:k.돌기?같은 것을 말하는 것같습니다.
sunnken:s.안으로 파인 모양
cap-surface(갓 표면)
fibrous:f.섬유, grooves:g.홈이 있는 표면, scaly:y.비늘표면,smooth=s.부드러움
cap-color(갓 색깔)
brown:n, buff:b.누런색, cinnamon:c.시나몬색 gray:g, green:r, pink=p,
purple:u, red:e, white:w, yellow:y
등등 위의 주소에 컬럼에 대한 설명이 있으니 궁금하신분들은 읽어보시길 바랍니다.
이에 대해 우리의 목표는 (classes: edible=e, poisonous=p) 식용,독인지를 분류하는 것이 목표입니다.
mushrooms<-read.csv('C:/Users/PJS/Documents/study/확률론/code/mushrooms.csv')
mushrooms %>% head()
mushrooms %>% str()
mushrooms %<>% mutate_all(as.factor) #모든 컬럼을 팩터로 변환
#stalk.root의 ?(결측치) 존재인식.####
#아예 제거.
mushrooms<-mushrooms %>% filter(mushrooms$stalk.root!='?')
#train/test 데이터 셋 분류
sam<-sample(1:nrow(mushrooms),size = nrow(mushrooms)*0.8,replace = F)
mushrooms_train <- mushrooms[sam,]
mushrooms_test <- mushrooms[-sam,]
#데이터셋에 있는 식용과 독의 비율은?
ggplot(data=mushrooms,aes(x=class))+
geom_bar(color='purple',lwd=1.3)
> #e,p의 비율
> ((mushrooms$class=='p') %>% sum)/nrow(mushrooms)
[1] 0.3819986
> ((mushrooms$class=='e') %>% sum)/nrow(mushrooms)
[1] 0.6180014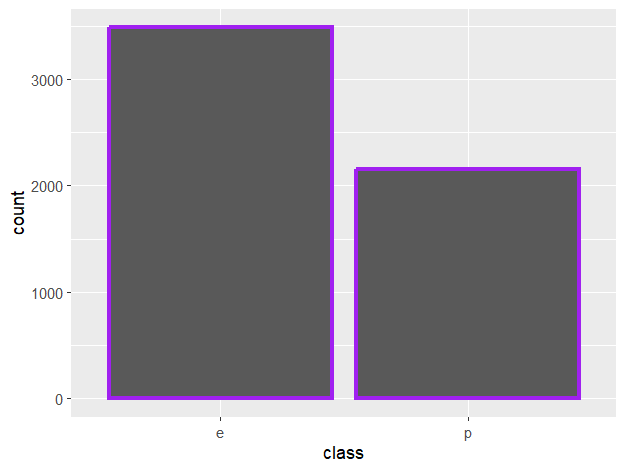
nb <- naiveBayes(class~ ., data = mushrooms_train)
mushrooms_test$pred <- predict(nb,mushrooms_test[,-1])
mushrooms_test %>% head()
#실제로 테스트 데이터마다 어떤 확률값으로 결정되었는가?
predict(nb,mushrooms_test[,-1],type='raw')
#정확도
(mushrooms_test$class == mushrooms_test$pred) %>% mean()
[1] 0.9486271
-출처: AI소프트웨어학과 이두호교수님 강의파일